Cyber risk is no longer an abstract concern but a tangible and omnipresent challenge that demands constant vigilance.
This guide provides a detailed, actionable framework for managing cyber risk. It integrates foundational knowledge with advanced strategies to keep your organization ahead of evolving threats.
What is Cyber Risk?
Cyber risk represents the potential for loss or harm from technology-related incidents. It encompasses infrastructure vulnerabilities, external threats, and the broader reputational and operational consequences of a cyber event.
Cyber risk arises from:
- Malicious Threats such as ransomware attacks and phishing scams.
- Human Errors that compromise data security.
- System Failures that disrupt confidentiality, integrity, or availability.
Cyber risk threatens the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information systems and data. It affects operational efficiency, sensitive assets, and interconnected third parties, including partners or vendors. Managing it effectively requires a proactive approach combining contextual risk assessments, robust security protocols, and continuous monitoring.
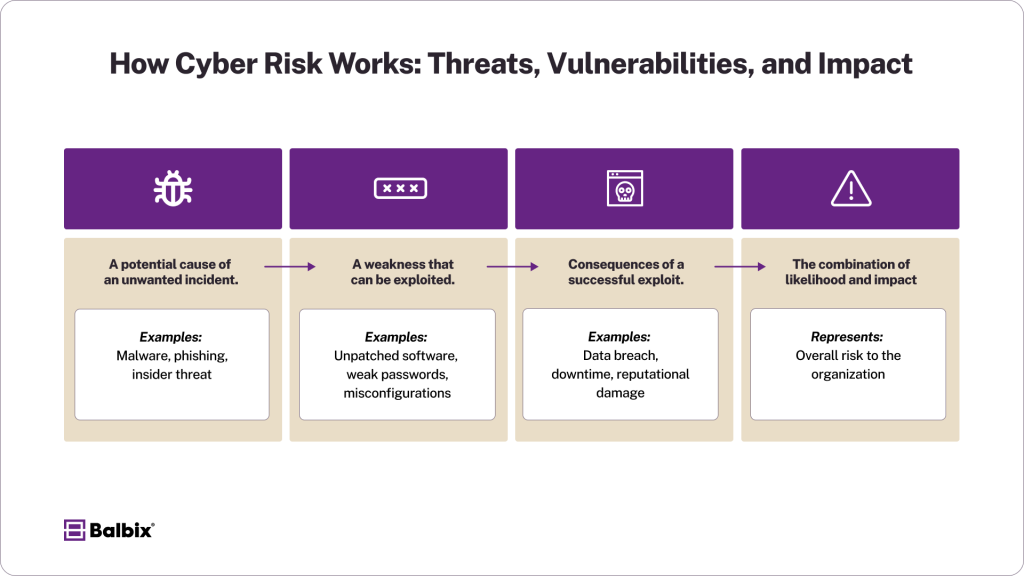
Breaking Down Cyber Risk
Understanding cyber risk involves dissecting its key components:
Threats
Threats are events or actions that could harm systems, data, or operations. Examples include:
- Ransomware encrypts critical data for ransom.
- Phishing tricks employees into divulging credentials.
- Insider Threats are caused by malicious or negligent employees.
Vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses in infrastructure, processes, or policies that threats exploit. Examples include poor password hygiene, misconfigured security settings, and unpatched software. Regular vulnerability assessments can help mitigate these entry points.
Impact
The consequences of exploited vulnerabilities range from financial losses and downtime to reputational damage, regulatory fines, and customer churn. Reducing impact is just as critical as minimizing exposure.
Common Cyber Risks
Effective risk planning starts by recognizing the most pervasive cyber risks:
- Ransomware Attacks halt operations until a ransom is paid, often with severe financial and reputational fallout.
- Phishing scams lure individuals into revealing sensitive information using deceptive messages.
- Insider threats stem from intentional sabotage or inadvertent mistakes.
- Third-party risks arise when vendors or partners introduce vulnerabilities, amplifying exposure.
Advanced Strategies for Managing Cyber Risk
Threat Intelligence Integration
Threat intelligence feeds enable real-time analysis of external threats. By cross-referencing internal logs with threat indicators, security teams can preemptively counteract incoming risks. Threat intelligence also enhances incident response through integration with SIEM and SOAR platforms, streamlining triage and mitigation efforts.
Leveraging AI and Machine Learning
AI and ML are indispensable for combating modern cyber risks. Key applications include:
- SOAR Automation accelerates alert handling and incident resolution while reducing MTTD and MTTR.
- Anomaly Detection uses ML to identify deviations in system behavior, revealing insider threats or zero-day vulnerabilities.
- Predictive Vulnerability Management ranks risks by severity, allowing prioritized remediation.
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA)
Zero trust eliminates implicit trust within networks, focusing on continuous verification:
- Micro-segmentation isolates sensitive resources, curbing lateral attacks during breaches.
- Least Privilege Access ensures users only access the resources necessary for their job.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) paired with behavioral analytics adds robust layers of security.
ZTA’s combination with AI amplifies capabilities, creating adaptive defenses that respond dynamically to emerging threats.
Measurable Metrics for Risk Management
Metrics provide clarity in articulating risk:
- MTTD (Mean Time to Detect) /MTTR (Mean Time to Resolve) track detection and response efficiency.
- FAIR (Factor Analysis of Information Risk) quantifies risk in financial terms, aligning mitigation budgets with business needs.
Regulatory Alignment
Compliance requirements like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA intersect with cyber risk management. Address obligations by automating data mapping, encryption, and real-time risk monitoring. This approach ensures security measures cover both regulatory compliance and broader risk exposure.
Advanced Risk Management Frameworks
Beyond NIST, frameworks like ISO 27005, COBIT, and CIS Controls guide risk mitigation:
- ISO 27005 structures risk assessments through a lifecycle approach, helping align actions with organizational priorities.
- COBIT bridges the gap between IT governance and cybersecurity strategy for integrated decision-making.
- CIS Controls focus on practical steps for quick improvements against common threats.
Actionable Steps for Proactive Risk Reduction
- Conduct Regular Risk Assessments: Identify evolving vulnerabilities using advanced threat modeling methodologies.
- Adopt Automation: Free up resources by automating repetitive operations with SOAR solutions.
- Implement ZTA: Prioritize least privilege, segmentation, and continuous identity verification.
- Align Frameworks with Goals: Use NIST, ISO 27005, and CIS Controls to enhance risk workflows.
- Train Employees: Cybersecurity is a team effort. A well-informed workforce bolsters your defenses.
Closing Thoughts
The goal remains consistent—reducing risk, limiting costs, and responding swiftly to incidents, empowering organizations to thrive amidst challenges.
Balbix helps organizations reduce cyber risk by continuously identifying and prioritizing the most critical vulnerabilities across their entire attack surface. By leveraging AI and machine learning, Balbix provides real-time risk quantification, enabling teams to focus remediation efforts where they matter most.
Its automated workflows streamline patching, ownership assignment, and policy enforcement, drastically improving response times. With comprehensive visibility and actionable insights, Balbix empowers security teams to manage risk and strengthen their cyber posture proactively.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is cyber risk, and why is it important to manage?
-
Cyber risk refers to the potential for financial loss, operational disruption, or reputational damage caused by technology-related threats, such as data breaches, ransomware attacks, or system failures. Managing cyber risk is essential because it protects sensitive data, ensures business continuity, and supports compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA.
- What are the most common types of cyber risks organizations face today?
-
The most common cyber risks include ransomware attacks, phishing scams, insider threats (both malicious and accidental), and third-party risks introduced by vendors or partners. If not properly mitigated, these risks can lead to data loss, service outages, and significant financial and reputational harm.
- How can organizations effectively manage and reduce cyber risk?
-
Effective cyber risk management requires a proactive approach that combines continuous risk assessments, threat intelligence, AI-powered tools like SOAR and anomaly detection, and frameworks such as NIST, ISO 27005, or CIS Controls. Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA), regular training, and automation are also key strategies to reduce exposure and respond quickly to threats.
- What role does AI play in modern cyber risk management?
-
AI enhances cyber risk management by automating detection and response, identifying anomalies, predicting vulnerabilities, and prioritizing threats based on potential impact. Solutions that use machine learning and SOAR help reduce mean time to detect (MTTD) and respond (MTTR), enabling faster and more accurate threat mitigation.
- Which cybersecurity frameworks help guide risk management strategies?
-
Several leading frameworks guide organizations in managing cyber risk effectively. NIST provides a comprehensive risk management process; ISO 27005 offers a lifecycle-based approach; COBIT connects governance to cybersecurity strategy; and CIS Controls offer prioritized, actionable practices for reducing common threats.